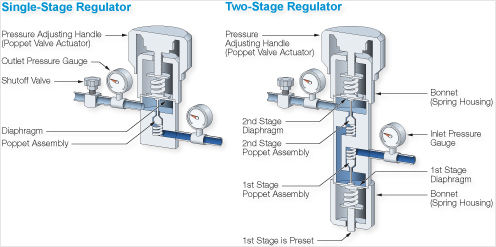
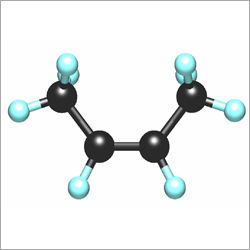
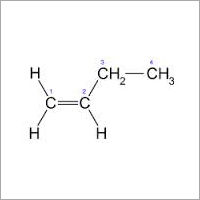
Product information Quality code 2.0 . Purity % volume >=99 Impurities ppm (where nothing else stated) Other CnHm 0.1.0% General information Filling pressure at 15 C bar: 2.3 Material recommendations: Gas: No restrictions Liquid: Avoid plastic and rubber. Characteristics Highly flammable liquefied colourless gas. Health risks Asphyxiating. Transport ADR Class 2 3(b). Physical data Molecular weight: 56.11 Boiling point at 1.013 bar C: -6.90 Density (1.013 bar 15 C) kg/m3: 2.45 Vapour pressure at 0 C bar: 1.34 20 C bar: 2.64 Flammability range in air % (volume): 1.8-9.6 Specific volume (1.013 bar 15 C) m3/kg: 0.408 Source Almost all commercially produced butenes are obtained as by-products catalytic or thermal cracking refinery processes which upgrade high fractions to gasoline and steam cracking which produces light olefins for chemical feedstocks hydrocarbons derived from natural gas or crude oil. The butenes obtained are withdrawn as a mixture from the C4-fraction. From this mixture butadiene and butanes are separated by extractive distillation. The remaining butenes cannot be separated by mere distillation because their boiling points are too close together. In a first step iso-butene is isolated either by etherification with methanol to form methyl tert-butylether (MTB) or by hydrating iso-butene to tert-butanol (TBA). In this step all other C components in the mixture remain unchanged. MTB and TEA can then be split by reversing synthesis to produce high purity iso-butene. Once the iso-butene content has been reduced recovery of high purity 1-butene is possible by fractionation. The remaining 2-butenes can be separated by molecular sieve absorption methods. Other commercial processes that are sometimes used to produce specific isomers or mixtures of butenes or both either directly or as by-products include: the oxirane process for making propylene oxide (-> iso-butene) the dehydrogenation of butane and iso-butane (-> 1-butene cis-2-butene trans-2- butene) the disproportionation of olefins (-> cis-2-butene trans-2-butene) the oligomerization of ethylene (-> 1-butene). AU or any of them may become useful feedstock sources should the need arise. Applications iso-Butene is mainly used as a chemical intermediate iso-Butene is also used in the production of acid and alkaline resistant rubber.