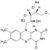
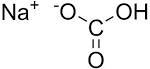
Sodium BicarbonateSodium BicarbonateSODIUM BICARBONATE is used in water-base muds as a source of bicarbonate ions to precipitate calcium and reduce pH. It is primarily used for treating cement contamination. Common names for SODIUM BICARBONATE (NaHCO3) are bicarbonate of soda bicarb and baking soda. It is a very weak base which is soluble in water and dissociates into sodium (Na) and bicarbonate (HCO3) ions in solution.Typical Physical PropertiesPhysical appearance- White powderSpecific gravity- 2.16pH (1% solution)- 8.3Solubility @ 86OF (30OC)- 11.1 g/100 ml waterBulk density- 50-68 Ib/ft3 (801-1089 kg/m3)ApplicationsSODIUM BICARBONATE is an economical and effective treatment for cement contamination. It precipitates calcium reduces pH and deflocculates cement-contaminated fluids. Cement contains calcium hydroxide (lime) and related compounds which increase pH and calcium concentration.These changes flocculate bentonite-based muds resulting in increased rheology and fluid loss. High pH and calcium can precipitate many common polymer additives particularly the acrylic-base polymers such as POLY-PLUST (PHPA) SP-101T and TACKLE.T Typical treatments with SODIUM BICARBONATE range from 0.5 to 2 lb/bbl (1.43 to 5.7 kg/m3). The amount of cement to be drilled and the degree of cement curing should be used as a basis for all treatments. Contamination with uncured "green" cement requires higher treatments. Treatments should be made on an incremental basis (usually 0.5 lb/bbl or 1.43 kg/m3) to prevent overtreatment which results in bicarbonate/ carbonate flocculation. Pretreatment is advisable for systems which are sensitive to cement contamination. A simplification of the chemical reactions for precipitating lime with SODIUM BICARBONATE is: Ca(OH)2 + NaHCO3 CaCO3 + NaOH + H2O When using SODIUM BICARBONATE to treat cement contamination: SODIUM BICARBONATE (lb/bbl) = Excess lime (lb/bbl) x 1.135 x Fw Where: Fw = Water fraction from retort analysis (% water/100) One pound (0.45 kg) of SODIUM BICARBONATE will remove 0.88 lb (0.4 kg) of lime which is roughly equivalent to 1.3 lb (0.6 kg) of cement. For every 1 lb (0.45 kg) of SODIUM BICARBONATE used to precipitate lime the equivalent of 0.48 lb (0.21 kg) of caustic soda (NaOH) remains as a byproduct. For severely contaminated muds a pH-reducing additive may be required to maintain the pH at a reasonable level. As an example 0.76 lb (0.35 kg) of citric acid (C6H8O7) would be required for every 1 lb (0.45 kg) of SODIUM BICARBONATE to maintain a constant pH. SODIUM BICARBONATE is most often used in combination with a pH-reducing additive and dilution to maintain acceptable properties. Other pH-reducing additives include TANNATHINT SPERSENE E SAPP gypsum and acetic acid. Bicarbonate ions begin converting to carbonate (CO3) ions when the pH increases above 8.3. Figure 1 illustrates the pH-dependent equilibrium relationships of bicarbonate carbonate and carbonic acid. Excess bicarbonate and carbonate ions flocculate muds and cause undesirable rheological and filtration properties. Avoid overtreatment!AdvantagesWidely available and is an economic treatment for cement contaminationConcentrated chemical; is effective at low treatment levelsReduces pH which helps maintain a reasonable pH in cement contaminated mudsNon-hazardous chemical and generally recognized as safeLimitationsUnless a low pH is desired Sodium Bicarbonate should not be used to treat soluble calcium in water-base muds and make up waters; soda ash should be reduce calcium and soften make up waterWhen treating severe cement contamination Sodium Bicarbonate will not reduce pH by itself; and acid or other pH-reducing additive should be used with Sodium Bicarbonate for these situationsOvertreatment results in bicarbonate or carbonate contamination. Even minor amounts of excess carbonate and bicarbonate ions can cause large increase in yield point gel strengths and fluid lossToxicity and HandlingBioassay information is available upon request. Handle as an industrial chemical wearing protective equipment and observing the precautions as described on the Transportation and Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS). SODIUM BICARBONATE is considered to be non-hazardous and is generally considered as safe. It is slightly alkaline which may cause mild irritation to eyes and skin. SODIUM BICARBONATE should be added slowly to the mud system by mixing through the hopper. Do not mix SODIUM BICARBONATE directly with acids or alkaline materials including citric or acetic acid caustic soda and limePackaging and StorageSODIUM BICARBONATE is packaged in 50- and 100-lb (22.7- and 45.4-kg) multi-wall paper sacks. SODIUM BICARBONATE is a globally available commercial chemical; other package sizes include: 25 40 45 and 50 kg (55 88 99 and 110 lb) and in various styles of paper or plasticsack containers. Store in a dry area away from water acids and alkaline chemicals.